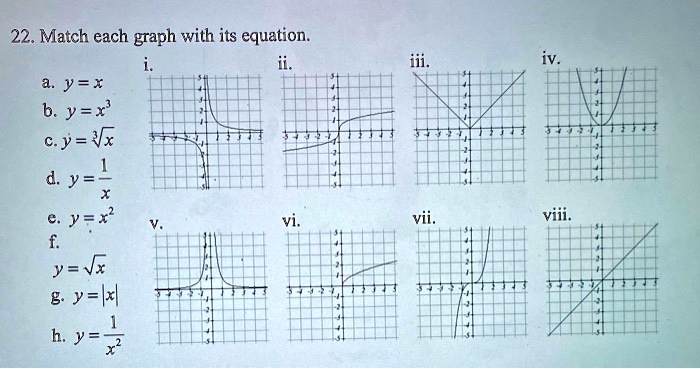
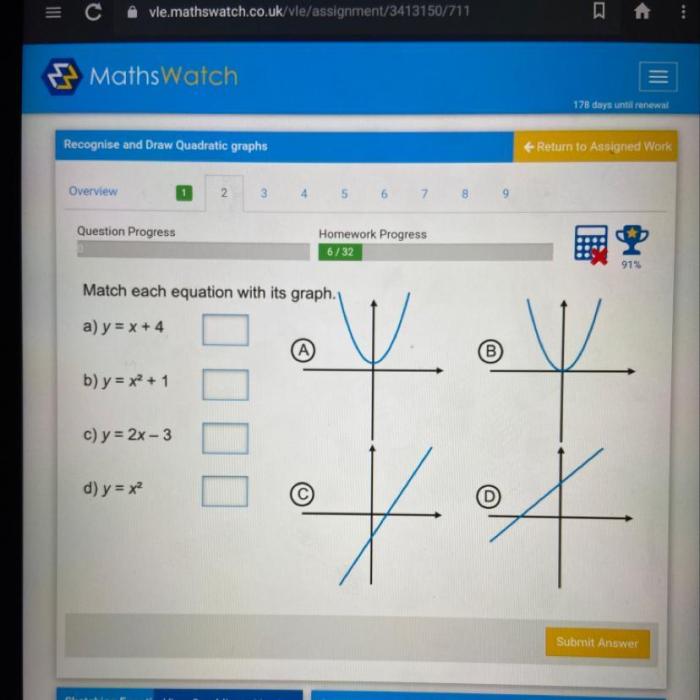
Match each table with its equation. – Match each table with its equation: a journey into the captivating realm where data and mathematical expressions intertwine. This exploration unveils the profound relationship between tabular representations and their corresponding equations, shedding light on how equations encapsulate the patterns and insights hidden within data.
Tables, with their structured rows and columns, provide a visual snapshot of data, while equations, with their concise mathematical language, offer a precise and generalizable representation of the underlying relationships. Understanding the connection between these two forms empowers us to extract meaningful insights from data, uncover hidden trends, and make informed decisions.
Table Equation Correlation

Tables and equations are powerful tools for representing and analyzing data. A table is a structured arrangement of data in rows and columns, while an equation is a mathematical expression that describes a relationship between variables.
The relationship between tables and equations is that an equation can be used to represent the data displayed in a table. For example, a table of sales data might show the number of units sold for each product in each month.
An equation could be used to represent the relationship between the number of units sold and the price of the product.
Table Structure Analysis
Tables are composed of several structural elements, including:
- Rows: Horizontal lines of data
- Columns: Vertical lines of data
- Headers: Labels that identify the data in each row or column
Tables can have different structures, depending on the data they represent. For example, a table of sales data might have rows for each product and columns for each month. A table of customer data might have rows for each customer and columns for their name, address, and phone number.
Equation Interpretation
Equations are composed of coefficients and variables. Coefficients are numbers that multiply variables, while variables are letters that represent unknown values.
To interpret an equation, we need to understand the meaning of the coefficients and variables. For example, in the equation y = mx + b, the coefficient m represents the slope of the line, and the coefficient b represents the y-intercept.
Table-Equation Alignment, Match each table with its equation.
Matching tables to their equations can be a challenging task. However, there are several key features that can help us make accurate matches.
- The number of rows and columns in the table should match the number of variables in the equation.
- The headers in the table should correspond to the variables in the equation.
- The data in the table should satisfy the equation.
Data Visualization
Tables and equations are both powerful tools for visualizing data. Tables can be used to display large amounts of data in a structured format, while equations can be used to represent complex relationships between variables.
By combining tables and equations, we can create powerful data visualizations that can help us to understand the underlying patterns and trends in our data.
User Queries: Match Each Table With Its Equation.
What is the significance of matching tables with equations?
Matching tables with equations allows us to derive generalizable insights from data, uncover hidden patterns, and make informed decisions based on mathematical relationships.
How can I identify the equation that corresponds to a given table?
To match a table with its equation, consider the structure of the table, the relationships between its rows and columns, and the underlying mathematical concepts that may be represented.
What are the common structural elements of tables?
Common structural elements of tables include rows, columns, headers, and footers, which organize and present data in a structured manner.