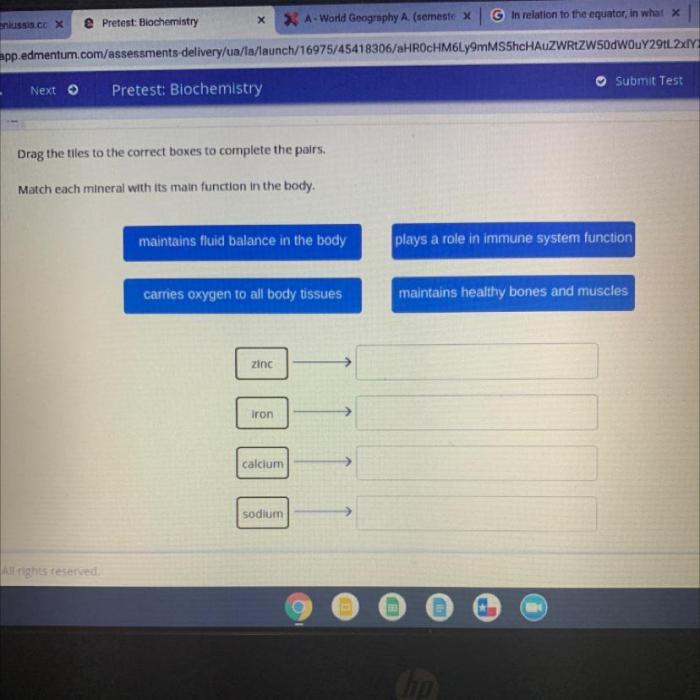
Match each mineral with its function in the human body. This topic delves into the intricate relationship between minerals and human health, exploring the diverse roles these essential elements play in maintaining our well-being.
From the structural integrity of our bones to the efficient transmission of nerve impulses, minerals are indispensable for a multitude of physiological processes. This article unravels the fascinating world of minerals, shedding light on their specific functions and the vital role they play in our overall health.
Mineral Functions in the Human Body: Match Each Mineral With Its Function In The Human Body.
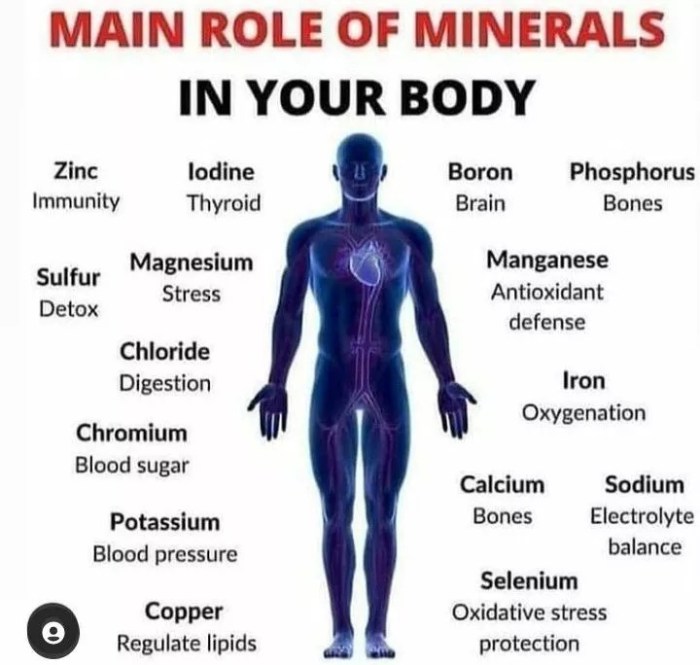
Minerals are essential for maintaining optimal human health. They play diverse roles in various bodily functions, including bone health, electrolyte balance, nerve function, energy metabolism, immune function, and cell growth.
The human body contains a wide range of minerals, each with specific functions:
Calcium: Bone Health and Beyond
Calcium is crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. It also plays a role in nerve transmission, muscle contraction, and blood clotting.
Iron: Oxygen Transport and Energy Production
Iron is essential for carrying oxygen throughout the body via hemoglobin. It is also involved in energy metabolism and red blood cell production.
Potassium: Electrolyte Balance and Nerve Function
Potassium is an important electrolyte that regulates fluid balance and nerve impulses. It also helps maintain blood pressure and heart rhythm.
Magnesium: Muscle Function and Energy Metabolism
Magnesium is essential for muscle relaxation and contraction. It is also involved in energy production and nerve function.
Sodium: Fluid Balance and Nerve Impulses
Sodium is an electrolyte that regulates fluid balance and nerve impulses. It also plays a role in maintaining blood pressure and hydration.
Zinc: Immune Function and Cell Growth
Zinc supports immune function and wound healing. It is also involved in cell growth, development, and metabolism.
Phosphorus: Bone Health and Energy Metabolism
Phosphorus is essential for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. It is also involved in energy metabolism and cell function.
Iodine: Thyroid Hormone Production
Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
Selenium: Antioxidant Protection and Immune Function, Match each mineral with its function in the human body.
Selenium has antioxidant properties and protects cells from damage. It is also involved in immune function and thyroid hormone metabolism.
Question Bank
What are the most important minerals for human health?
Calcium, iron, potassium, magnesium, sodium, zinc, phosphorus, iodine, and selenium are among the most essential minerals for human health.
How do I know if I am getting enough minerals?
A balanced diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein should provide you with the minerals you need. However, if you have any concerns, you can talk to your doctor about taking a mineral supplement.
What are the symptoms of mineral deficiency?
Symptoms of mineral deficiency can vary depending on the mineral. However, some common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, muscle cramps, and brittle bones.