Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive DNA and Genetics Lesson 3 Answer Key. Delve into the intricate world of DNA, unraveling its structure, replication, and role in genetic expression. This guide illuminates the fundamentals of genetics, empowering you to decipher the blueprint of life.
Our exploration unveils the building blocks of DNA, the intricate dance of base pairing, and the remarkable process of DNA replication. We decipher the secrets of transcription and translation, unlocking the genetic code that governs our traits. Along the way, we uncover the nature of mutations, their impact on our health, and the cutting-edge technologies that harness the power of genetics.
DNA Structure
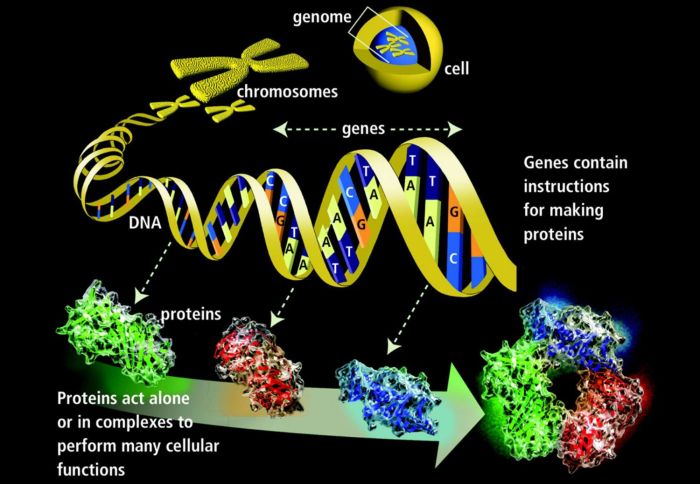
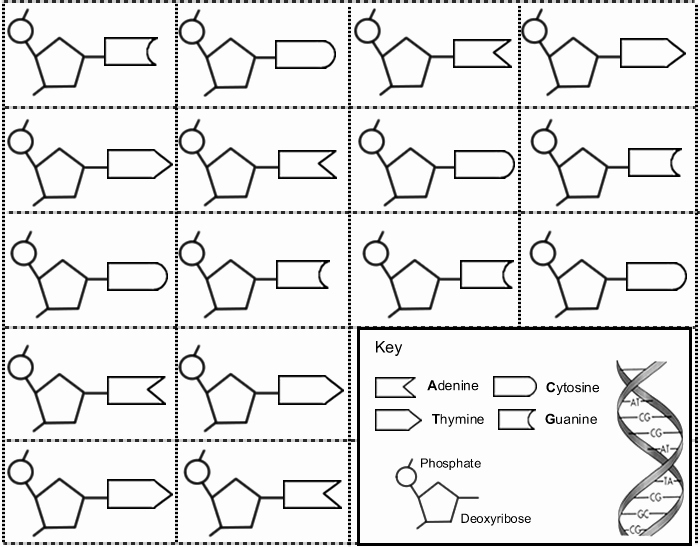
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is made up of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These nucleotides are arranged in a specific order, which determines the genetic code.
The DNA molecule is a double helix, which means it has two strands that are twisted around each other. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nucleotides. The A-T nucleotides form two hydrogen bonds, while the C-G nucleotides form three hydrogen bonds.
DNA Replication, Dna and genetics lesson 3 answer key
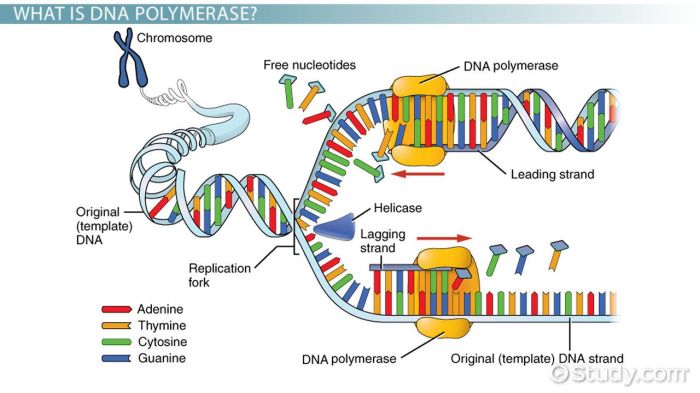
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, as each new cell needs its own copy of the DNA.
DNA replication begins when the DNA double helix unwinds and the two strands separate. Each strand then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand. The enzyme DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new strand, matching them to the complementary nucleotides on the template strand.
Transcription
Transcription is the process by which DNA is used to make RNA. RNA is a molecule that is similar to DNA, but it has a different structure and function. RNA is used to carry the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are made.
Transcription begins when the enzyme RNA polymerase binds to a promoter region on the DNA. The RNA polymerase then moves along the DNA, unwinding the double helix and transcribing the DNA sequence into RNA.
Translation
Translation is the process by which RNA is used to make proteins. Proteins are essential for the structure and function of cells.
Translation begins when the ribosome binds to the mRNA. The ribosome then moves along the mRNA, reading the sequence of codons. Each codon codes for a specific amino acid. The ribosome adds the correct amino acid to the growing protein chain.
Mutations
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence. Mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental toxins, radiation, and errors during DNA replication.
Mutations can have a variety of effects on the organism. Some mutations are harmful, causing genetic diseases or developmental problems. Other mutations are neutral, having no effect on the organism. Still other mutations are beneficial, giving the organism an advantage in its environment.
Genetic Technologies
Genetic technologies are a rapidly growing field of research and development. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize medicine, agriculture, and forensics.
Some of the most important genetic technologies include:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction): PCR is a technique that can be used to amplify a specific region of DNA. This technique is used in a variety of applications, including DNA fingerprinting and genetic testing.
- DNA sequencing: DNA sequencing is a technique that can be used to determine the order of the nucleotides in a DNA molecule. This technique is used in a variety of applications, including genetic research and medical diagnosis.
- Genetic engineering: Genetic engineering is a technique that can be used to change the DNA of an organism. This technique is used in a variety of applications, including the development of genetically modified crops and the treatment of genetic diseases.
Answers to Common Questions: Dna And Genetics Lesson 3 Answer Key
What are the components of DNA?
DNA is composed of nucleotides, each consisting of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
How does DNA replicate?
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process where each original strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand, resulting in two identical double-stranded DNA molecules.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to specific DNA sequences called promoters and unwinds the DNA double helix, allowing for the synthesis of a complementary RNA molecule.