How theremin music sounds crossword? Dive into the captivating world of the theremin, an electronic instrument that produces ethereal and otherworldly melodies. Its unique characteristics and distinctive sound have captivated musicians and audiences alike, leaving an indelible mark on popular culture.
From its historical origins to its innovative techniques, this article unravels the mysteries of theremin music, exploring its distinctive sound, notable musicians, and impact on the evolution of electronic music.
Historical Context of the Theremin

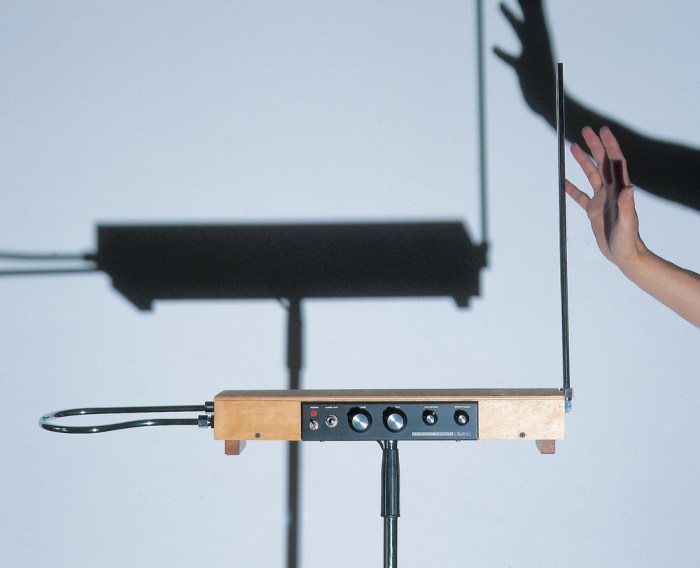
The theremin, an electronic musical instrument, was invented by Russian physicist Leon Theremin in 1920. It is unique in that it is played without physical contact, using only hand movements in proximity to two metal antennas. The theremin’s ethereal and otherworldly sound has made it a popular choice for film and television scores, as well as for experimental and electronic music.
The theremin produces sound through the interaction of the player’s hands with two metal antennas. The left antenna controls the pitch of the sound, while the right antenna controls the volume. The player’s hands act as capacitors, changing the capacitance of the antennas and thus affecting the frequency and amplitude of the sound waves produced.
Early Uses of the Theremin, How theremin music sounds crossword
The theremin was first used in musical performances in the 1920s. It quickly gained popularity as a novelty instrument, and was featured in several films and radio broadcasts. In the 1930s, the theremin was used in a number of classical music compositions, including Edgard Varèse’s “Ionisation” and Dmitri Shostakovich’s “Lady Macbeth of the Mtsensk District.”
However, the theremin’s popularity waned in the 1940s, due in part to the rise of the synthesizer.
Theremin Music Characteristics
Theremin music is renowned for its ethereal, otherworldly sound. The instrument’s unique design allows for a wide range of pitches and timbres, creating a captivating and expressive musical experience.
Pitch and Timbre Manipulation
The theremin produces sound through the movement of the performer’s hands in proximity to two metal antennas. The left hand controls the pitch by moving closer or further from the pitch antenna, while the right hand controls the volume by moving towards or away from the volume antenna.
The theremin’s distinctive vibrato effect is created by the performer’s natural hand movements. By slightly wavering the hands, the pitch and volume can be subtly modulated, adding depth and character to the sound.
Notable Theremin Musicians
Over the years, several notable theremin musicians have emerged, each contributing to the development and popularity of the instrument.
- Clara Rockmore: A pioneering theremin virtuoso, Rockmore was known for her exceptional control and expressive playing. Her performances showcased the instrument’s versatility and lyrical qualities.
- Leon Theremin: The inventor of the theremin, Theremin was also an accomplished musician. His performances demonstrated the instrument’s technical capabilities and inspired many aspiring thereminists.
- Lydia Kavina: A Russian thereminist, Kavina expanded the instrument’s repertoire through her innovative compositions and collaborations with contemporary composers.
Theremin in Popular Culture

The theremin has found its niche in popular culture, particularly in the realm of film and television soundtracks, adding an ethereal and otherworldly element to cinematic experiences.
Film Scores and Television Soundtracks
The theremin’s unique sound has captivated filmmakers and composers, who have employed it to create haunting and evocative atmospheres in classic films such as The Day the Earth Stood Still(1951), Forbidden Planet(1956), and The Thing from Another World(1951). In television, the theremin has made memorable appearances in the iconic theme music for the sci-fi series Lost in Space(1965-1968) and the supernatural drama Twin Peaks(1990-1991).
Iconic Theremin Performances in Popular Music
Beyond film and television, the theremin has also made its mark in popular music. Clara Rockmore, a renowned theremin virtuoso, popularized the instrument in the mid-20th century with her captivating performances of classical and experimental works. In recent years, contemporary musicians such as Radiohead, The Beach Boys, and Sigur Rós have incorporated the theremin into their music, adding a unique and otherworldly touch to their compositions.
Impact on Electronic Music
The theremin’s pioneering role in electronic music cannot be overstated. As one of the earliest electronic instruments, it paved the way for the development of synthesizers and other electronic instruments that have become staples in modern music production. The theremin’s influence can be heard in the experimental electronic music of the 1950s and 1960s, and its legacy continues to inspire electronic musicians today.
Crossword Puzzle Clues
Crossword puzzles often include clues related to theremin music. These clues can test a solver’s knowledge of the instrument, its history, and its use in popular culture.
The following table provides a sample of crossword puzzle clues related to theremin music, along with their answers and explanations:
| Clue | Answer | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| “Electronic instrument played without touching” | Theremin | The theremin is an electronic musical instrument that is played by moving one’s hands in the air near two metal antennas. |
| “Soviet inventor of the theremin” | Leon Theremin | Leon Theremin was a Soviet inventor who invented the theremin in 1928. |
| “Film score that prominently featured the theremin” | The Day the Earth Stood Still | The theremin was used prominently in the film score for the 1951 science fiction film The Day the Earth Stood Still. |
| “Band that used the theremin in their song ‘Good Vibrations'” | The Beach Boys | The Beach Boys used the theremin in their 1966 song “Good Vibrations.” |
| “Type of music that often uses the theremin” | Electronic music | The theremin is often used in electronic music, which is a genre of music that is created using electronic instruments. |
Additional Resources
To further explore the fascinating world of theremin music, a wealth of resources is available both online and in print.
Online Resources
- Theremin World: A comprehensive website dedicated to all things theremin, featuring articles, tutorials, and a vibrant community forum.
- Thereminvox: An online community for theremin enthusiasts, offering a forum, tutorials, and a marketplace for instruments and accessories.
- YouTube: A vast collection of theremin performances, tutorials, and documentaries, showcasing the instrument’s unique capabilities.
Books
- The Theremin: A Musical Odysseyby Albert Glinsky: A definitive history of the theremin, its inventors, and its impact on music.
- The Theremin Handbookby Peter Pringle: A practical guide to playing and maintaining the theremin, with technical insights and historical context.
li> Theremin: Ether Music and Beyondby Thomas Grillo: An exploration of the theremin’s use in various musical genres, from classical to electronic.
Documentaries
- Theremin: An Electronic Odyssey(2000): A critically acclaimed documentary that traces the history of the theremin and its pioneers.
- The Singing Machine(2000): A documentary that features thereminist Lydia Kavina and her unique approach to the instrument.
Key Questions Answered: How Theremin Music Sounds Crossword
What is the theremin?
The theremin is an electronic instrument that is played without physical contact. It produces sound by manipulating electromagnetic fields around two metal antennas.
How does the theremin produce sound?
The theremin produces sound when the performer’s hands move closer to or farther from the metal antennas. The distance between the hands and the antennas changes the capacitance of the circuit, which in turn changes the pitch and volume of the sound.
Who invented the theremin?
The theremin was invented by Russian physicist Leon Theremin in 1920.
What are some famous theremin musicians?
Some famous theremin musicians include Clara Rockmore, Samuel Hoffman, and Lydia Kavina.